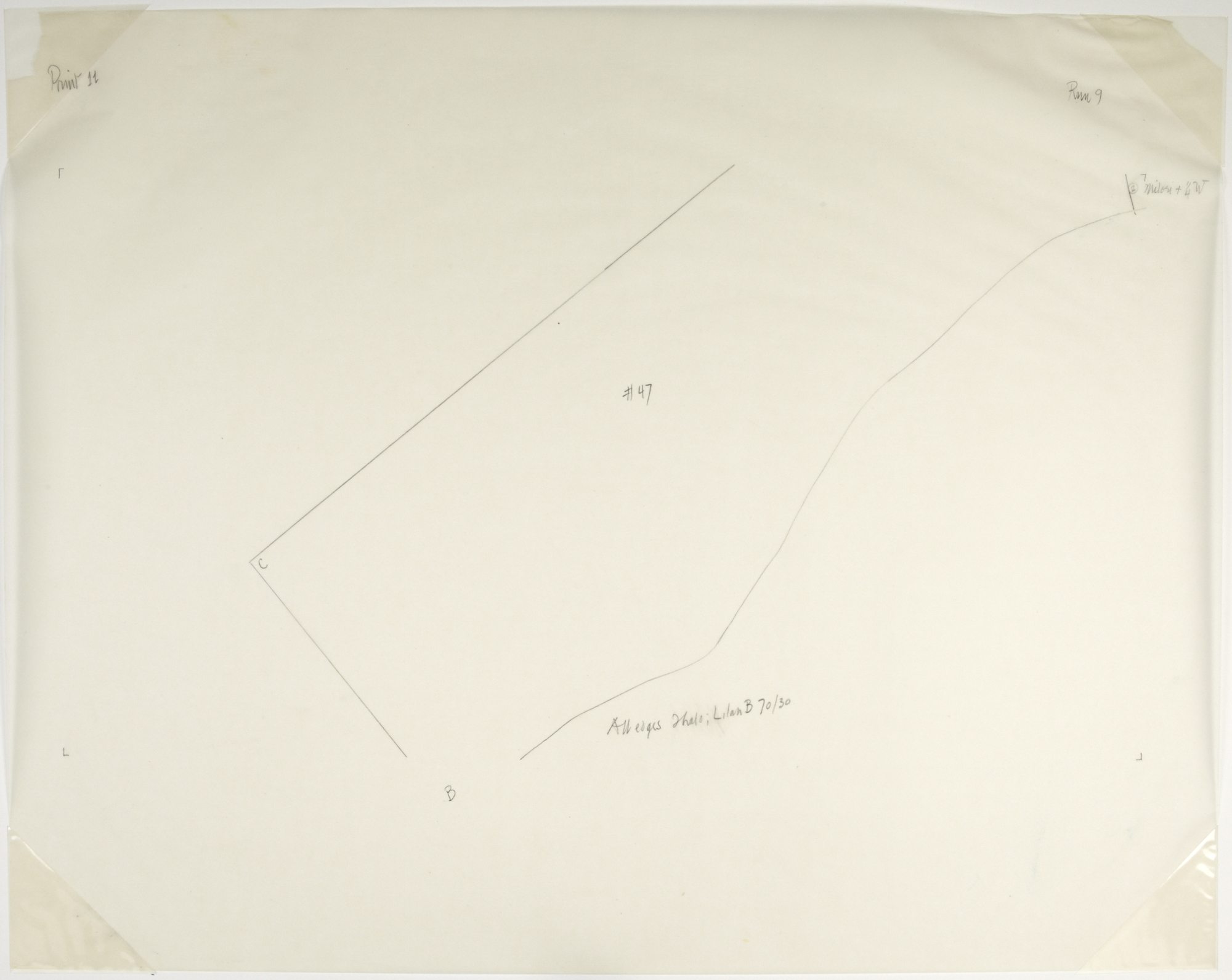
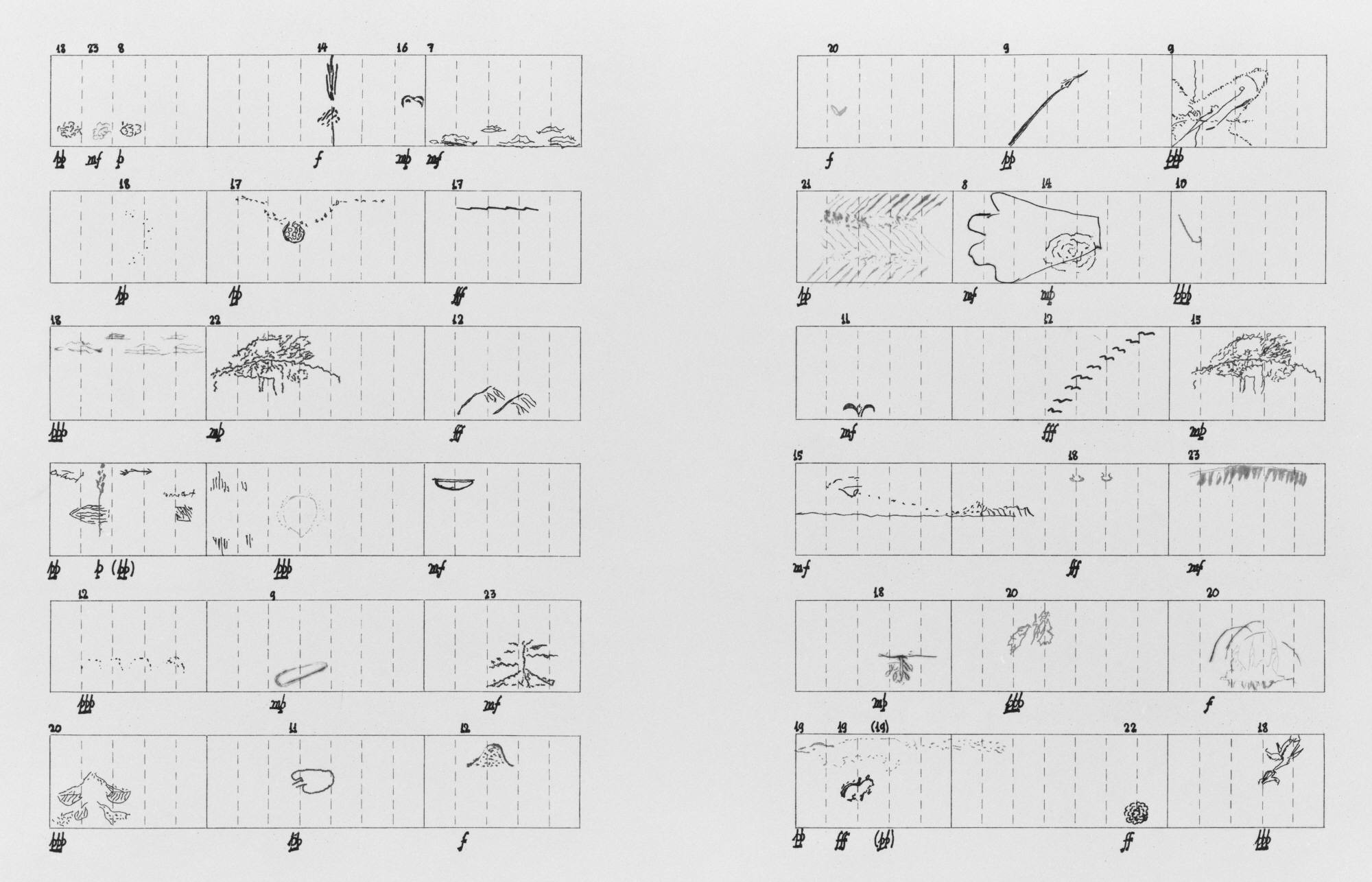
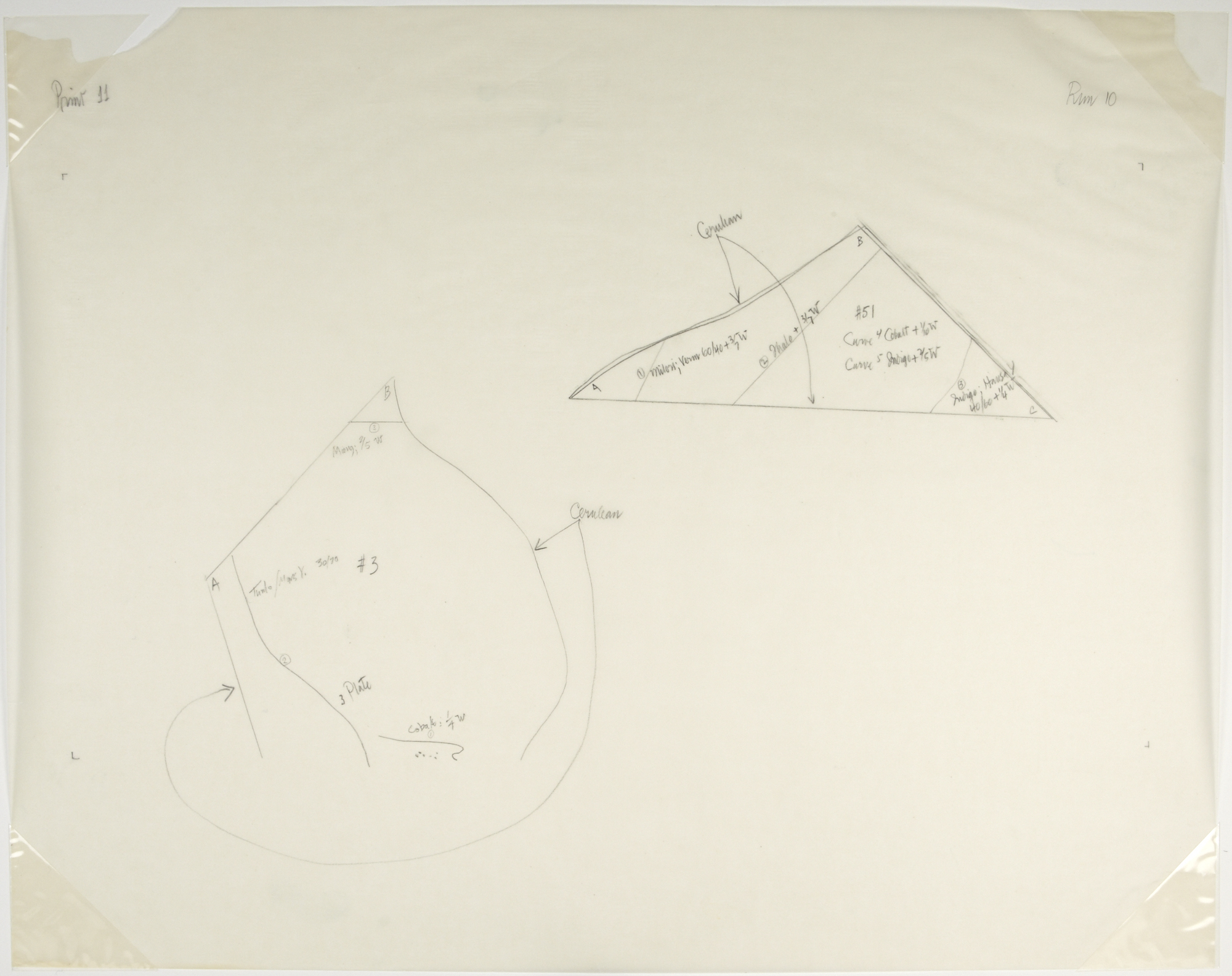
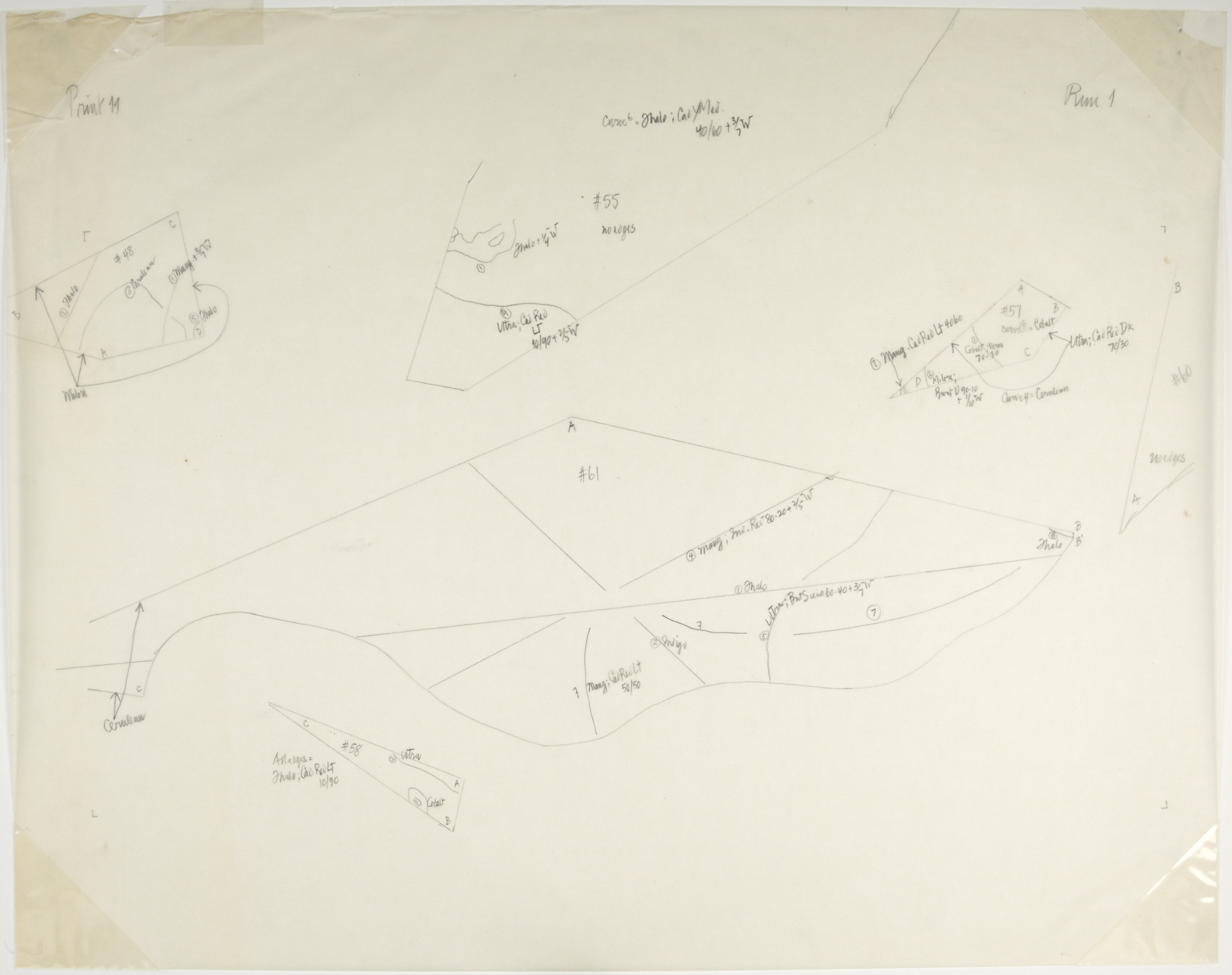
John Cage
Originally trained as an abstract painter, Cage abandoned the medium in favor of composition, which he studied with Henry Cowell and Arnold Schoenberg. In the 1940s, becoming interested in expanding the range of percussive instruments, he developed the "prepared piano", composing works for a piano with various objects placed between the strings. After studying Zen Buddhism, Cage began to work toward a new theory of composition, focusing on removing intention and personal taste, with attention paid to the process and the element of chance. Regarding silence on equal terms as structured sound and noise, in 1952 Cage produced 4'33", a composition in which no sound is made. Cage was a strong influence and a collaborator with many visual artists. American composer (ULAN).